Introduction
Knee Pain When Bending is a common issue that affects people of all ages, from active individuals to those leading a more sedentary lifestyle. Whether it’s a sharp pain while squatting, discomfort during routine activities, or stiffness when climbing stairs, this problem can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
The causes of knee pain range from simple overuse and minor injuries to more serious conditions like arthritis or ligament damage. Understanding these knee pain causes is crucial for finding effective relief and preventing further complications.
Fortunately, there are numerous ways to address and manage knee pain, including targeted knee exercises to strengthen the muscles around the joint and medical options for knee injury treatment.
In this blog, we’ll explore the common causes of knee pain when bending, practical prevention tips, and effective treatment options to help you regain mobility and maintain healthy knees. Whether you’re dealing with mild discomfort or chronic pain, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to take proactive steps toward recovery.
Common Causes of Knee Pain When Bending
Experiencing knee pain when bending can be frustrating and disruptive, especially when it limits everyday activities like walking, sitting, or exercising. Identifying the root causes is the initial step in achieving effective relief. Below are some common knee pain causes that could explain why bending your knee is painful.
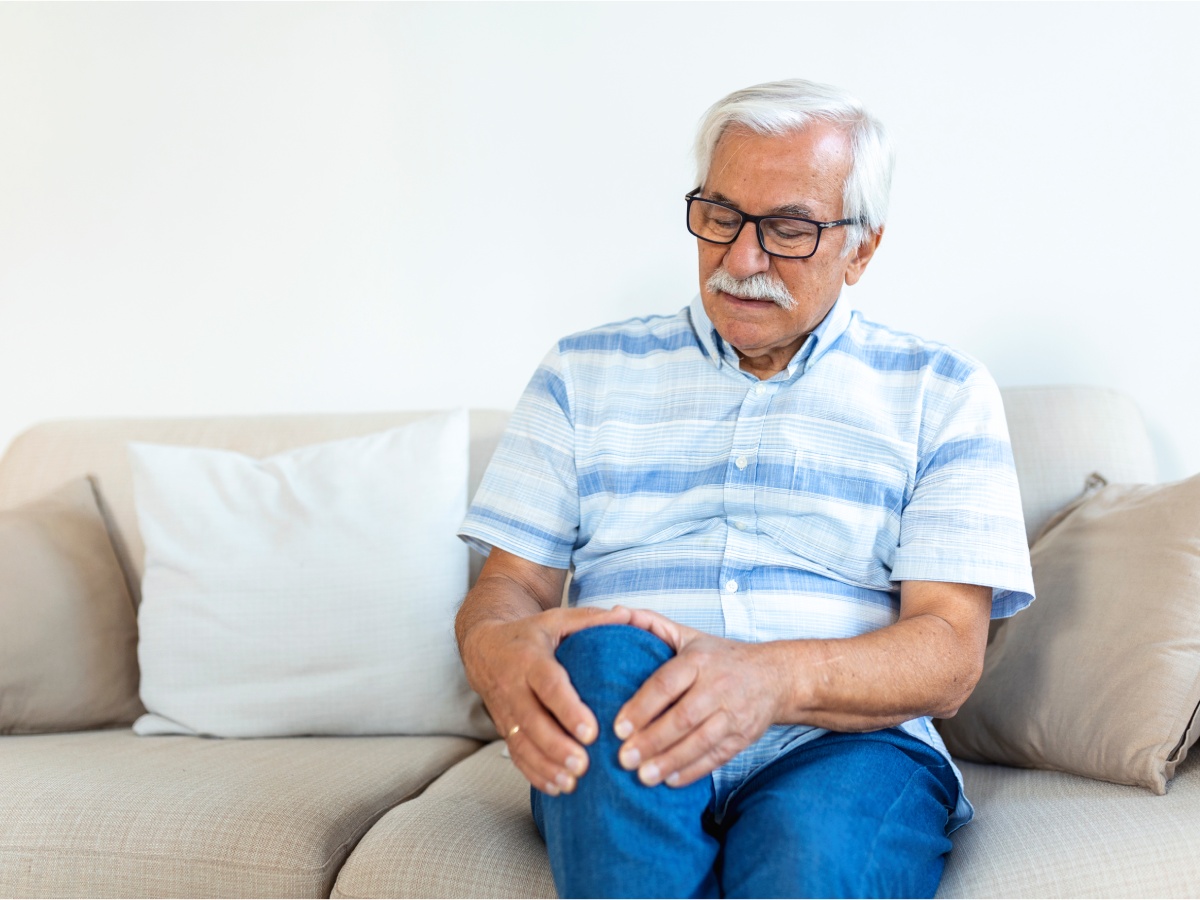

1. Overuse or Strain
Overusing your knees during repetitive activities like running, jumping, or squatting can lead to pain. When the joint is subjected to excessive stress without adequate rest, it can cause inflammation in the tendons and surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort while bending.
2. Ligament Injuries
The knee relies on vital ligaments like the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) and MCL (medial collateral ligament) for stability. Sudden movements, falls, or high-impact activities can result in sprains or tears, causing sharp pain when bending or straightening the knee.
3. Meniscus Tear
The meniscus serves as a shock absorber between the thigh and shin bones. A sudden injury or chronic wear can cause a tear, leading to swelling, pain, and stiffness, especially when the knee is bent or moved in certain ways.
4. Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: This condition involves the gradual deterioration of cartilage in the knee joint, commonly seen in older adults. As the cushioning wears away, bending the knee can become painful.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the knee.
5. Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Inflammation in the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone can result in localized pain. This is often seen in athletes who participate in high-impact sports like basketball or volleyball, causing discomfort during activities such as kneeling, bending, or squatting.
6. Bursitis
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction within the knee joint. When these sacs become inflamed due to repetitive motion or injury, bursitis occurs, causing pain and swelling, especially when the knee is bent or under pressure.
7. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner’s Knee)
This condition, often caused by improper alignment of the kneecap or overuse, leads to discomfort around the front of the knee. Bending the knee, climbing stairs, or sitting for extended periods can aggravate the pain.
8. Gout or Other Joint Infections
Gout and other joint infections, such as bacterial arthritis, can lead to severe, sudden pain in the knee. This is particularly noticeable when bearing weight or bending the knee.
9. Muscle Weakness or Imbalance
Weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee, such as the quadriceps or hamstrings, can place additional stress on the joint. This imbalance often results in pain during bending and underscores the need for targeted knee-strengthening exercises.
10. Cartilage Damage or Degeneration
Over time, the cartilage in the knee joint can degrade due to injury or the aging process. This condition, called chondromalacia patella, can cause pain during knee movement and a grinding or clicking sensation.
Signs to Watch for When Experiencing Knee Pain During Bending
If you are dealing with knee pain when bending, it is crucial to pay attention to specific symptoms that can help identify the cause of your discomfort. Recognizing these early signs can help you seek the right treatment and avoid further complications. Below are some key symptoms to keep an eye on:

-
Swelling and Stiffness
Swelling around the knee joint often signals inflammation, which can result from an injury, arthritis, or overuse. Stiffness is commonly experienced after prolonged periods of rest, such as after waking up or sitting for an extended time, and it can make it harder to bend the knee.
-
Pain During Movement
Sharp or dull pain when bending, squatting, or kneeling is a clear indication of an underlying problem. The discomfort may worsen when climbing stairs or standing up after sitting for long periods.
-
Popping or Clicking Noises
Hearing clicking or popping sounds when you move your knee may suggest cartilage damage, such as a meniscus tear, or misalignment of the kneecap. If these noises are accompanied by pain, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
-
Difficulty Bearing Weight
Struggling to walk or stand without pain when bending your knee may point to a ligament injury or significant inflammation. This symptom is concerning and may require immediate medical attention.
-
Persistent Pain at Rest
If your knee continues to hurt even when not in use, this could be a sign of chronic conditions like arthritis or bursitis. This type of pain is often described as dull or throbbing, and it may be more intense during the night.
-
Redness or Warmth Around the Joint
Redness, warmth, or tenderness in the knee can be signs of infection, gout, or intense inflammation. These symptoms should not be ignored and require prompt medical attention.
-
Knee Locking or Giving Way
If your knee locks up or feels unstable when you bend or put weight on it, it could indicate ligament tears or loose cartilage. This symptom often requires professional diagnosis and intervention.
-
Limited Knee Mobility
Difficulty bending or straightening the knee could signal joint damage, muscle tightness, or conditions like arthritis or a meniscus tear. A reduced range of motion can interfere with daily movements and tasks.
-
Numbness or Tingling
Tingling or numbness around the knee or lower leg may indicate nerve issues, which are often caused by injury or swelling. This symptom requires medical attention to determine the appropriate course of action.
When to Seek Medical Help
If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, especially when combined with others, it’s important to seek professional advice. A healthcare provider can help determine the cause of your knee pain and recommend suitable treatments, such as physical therapy, exercises, or medical interventions.
By identifying these symptoms early, you can take steps to manage your knee pain effectively and protect your joint health.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you notice knee pain while bending, it’s important to recognize when professional medical advice is necessary. While some knee issues can be managed with at-home care, others may require professional diagnosis and treatment.
Red Flags to Watch For
Severe Swelling:
Sudden or persistent swelling could indicate a ligament tear, infection, or other serious conditions.
Inability to Move the Knee: Stiffness or locking that limits your range of motion may signal structural damage like a meniscus tear.
Persistent Pain:
Pain that lingers or worsens over time, despite rest and self-care, should not be ignored.
Instability:
If your knee feels like it might give way when walking or standing, it’s time to consult a specialist.
Visible Deformity or Bruising:
These signs could point to a fracture or significant injury requiring immediate attention.
Timely medical evaluation can help prevent further complications and ensure the best course of treatment is implemented.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
Accurate diagnosis is essential to address the underlying knee pain causes effectively. Here’s what you expect during the diagnostic process:
Physical Examination
Doctors typically start by:
- Assessing the knee’s range of motion and stability.
- Checking for swelling, tenderness, or warmth around the joint.
- Asking about your activity levels, recent injuries, or specific instances that trigger pain.
Imaging Tests
To get a clearer view of the knee’s structure, doctors may recommend:
- X-Rays: To detect fractures or joint misalignments.
- MRI Scans: To assess soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
- Ultrasounds: To examine fluid buildup or inflammation around the knee.
Lab Tests
In cases where gout, infection, or autoimmune conditions are suspected, doctors may:
- Conduct blood tests to check for markers of inflammation or infection.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain When Bending
Once the cause of your knee pain is identified, a combination of treatments can help alleviate symptoms and restore function.
At-Home Remedies
- RICE Method: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation are effective for reducing swelling and easing mild pain.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort and inflammation.
Physical Therapy
- A trained therapist can guide you through knee exercises designed to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve flexibility, and support the joint.
- Common exercises include leg lifts, hamstring stretches, and balance training.
Medical Treatments
- Corticosteroid Injections: These reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief for severe pain.
- Prescription Medications: For conditions like arthritis, specialized drugs may be prescribed.
- Surgical Options: Procedures like arthroscopy, cartilage repair, or knee replacement are reserved for severe cases where other treatments fail.
Preventing Knee Pain
Prevention is always better than treatment, and adopting the following habits can help protect your knees in the long term:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight places added stress on the knees, leading to increased wear and tear. Keeping a healthy BMI helps reduce this pressure. - Strengthen Muscles Around the Knee
Incorporate exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg lifts into your fitness routine to build muscle strength and provide better support for the knee joint. - Improve Flexibility
Regularly stretching the hamstrings, quadriceps, and calves helps maintain flexibility, reducing stiffness and promoting a better range of motion. - Proper Footwear
Choose shoes that offer good support, cushioning, and stability during daily activities and sports to protect your knees. - Avoid Overloading the Knees
Be mindful of your technique when lifting heavy objects or participating in high-impact activities to prevent unnecessary strain on the knees.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Knee Health
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices can keep your knees functioning well for years to come:
- Balanced Nutrition: Focus on foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids to support joint health.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain joint lubrication and reduces friction during movement.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension, indirectly affecting joint health. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Exercises for Relieving Knee Discomfort
Consistent movement is key to preventing knee stiffness and promoting better joint function. These exercises can help reduce discomfort in your knees, especially when bending:
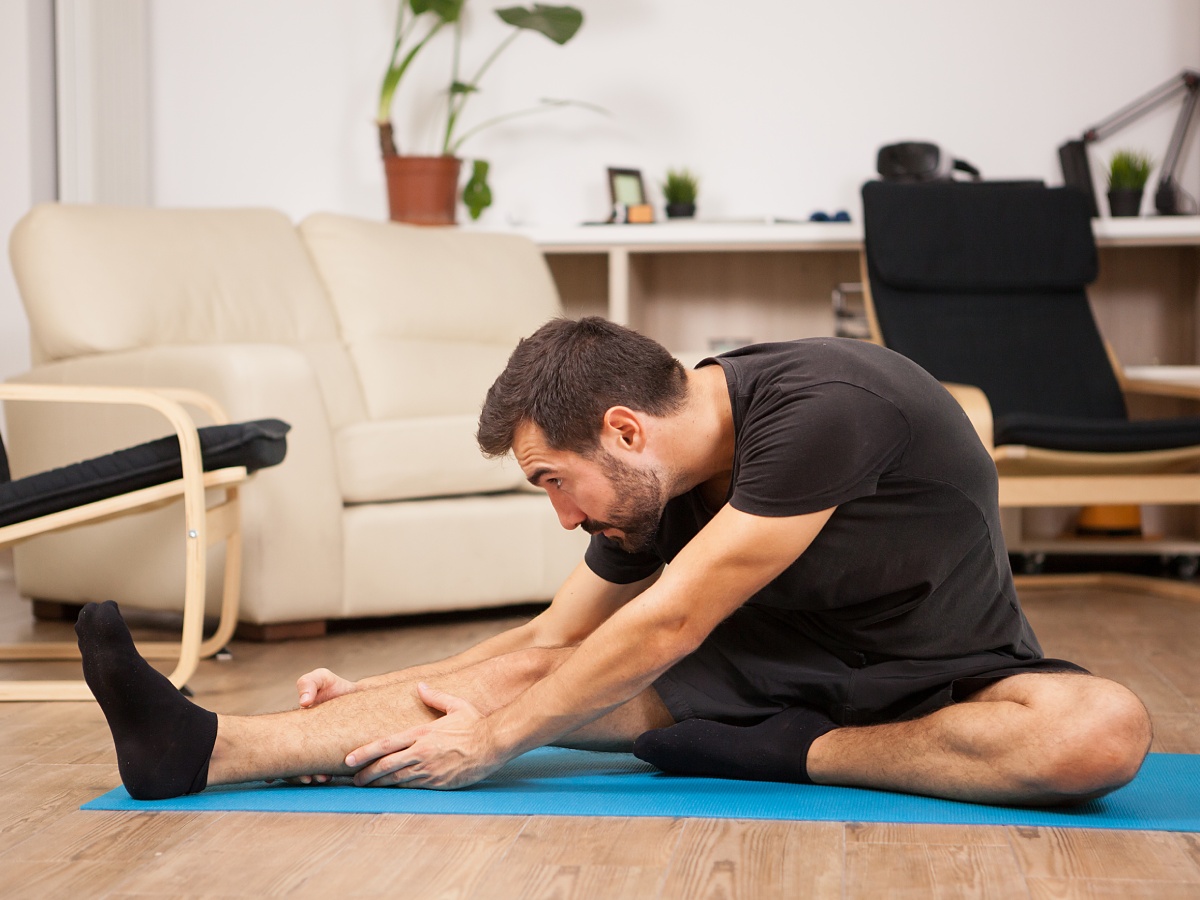

Low-Impact Exercise Options
Try activities such as gentle swimming, biking, or walking. These forms of exercise are easy on the knees, helping to strengthen the muscles around the joint without putting excess strain on them.
Gentle Stretches for Knee Relief
- Hamstring Stretch: While sitting on the floor, extend one leg straight out. Reach toward your foot to stretch the back of your thigh, holding the position to feel the stretch.
- Quadriceps Stretch: Stand tall, balancing on one leg. Grab the opposite ankle and gently pull it toward your body, stretching the front of your thigh.
Helpful Yoga Poses
- Child’s Pose: This restorative pose helps to release tension in the knees and lower back.
- Warrior Pose: Strengthens the legs, improving balance and offering support to the knee joint.
Sample Exercise Routine
- Begin by walking slowly for a few minutes to get your body moving.
- Complete 3 sets of 10 leg raises on each side to target the muscles supporting the knee.
- Hold a quad stretch for 20 seconds per leg to release tension in the thighs.
- Finish your routine with a calming hamstring stretch to relax the muscles.
By regularly practicing these exercises, you can reduce knee pain and enhance overall joint health
Conclusion
Addressing knee pain when bending promptly is crucial to maintaining your mobility and overall quality of life. Ignoring persistent pain or discomfort can lead to more serious issues, making early intervention key to preventing long-term complications.
By understanding the common knee pain causes and recognizing the warning signs, you can take proactive steps to protect your knees. Incorporating regular knee exercises into your routine, maintaining a healthy weight, and using proper techniques during physical activities can help prevent unnecessary strain on the joint.
If your pain persists or worsens despite at-home remedies, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to effectively manage knee pain and support joint health.
Your knees are integral to your daily life, and with the right care and prevention strategies, you can ensure they remain strong and pain-free for years to come.
Also Read: HIV Cure: Latest Advancements in Research









3 Responses